RDF Basics
See also: 002-exploring-oz-dev-log
Resources
Basics#
RDF
- at a general level - can be used to represent information about things that can be identified on the web - even if not on the web.
- intended to be used by applications, rather than people
RDF's basic concept is that things are
- identified using URIs; and
- described using simple properties and property values.
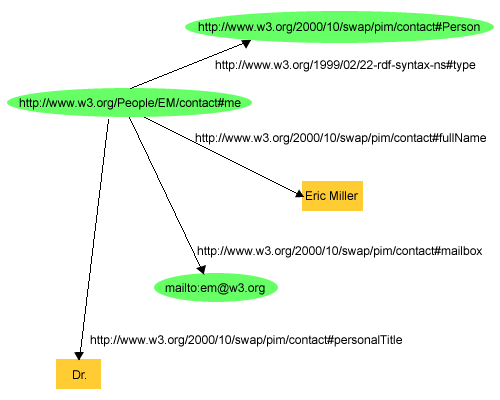
Data takes the form of a graph of nodes and arcs. For example, the following statements becomes the figure below
"there is a Person identified by http://www.w3.org/People/EM/contact#me, whose name is Eric Miller, whose email address is em@w3.org, and whose title is Dr."
Where nodes are URIs the args (properties) are also URIs and values of properties are different types of "nodes" containing values
The RDF model#
A statement consists of three parts
- subject what the RDF statement is about
- predicate - identifies/labels the property of the subject the statement is talking about
- object - the value of the property
subject and object form nodes. The predicate is the arc joining the nodes.
subject and predicate typically URIs. object can be a URI or a literal value (e.g. string, number, date)
Statements can be represented visually as graphs, or as triples (subject, predicate, object)